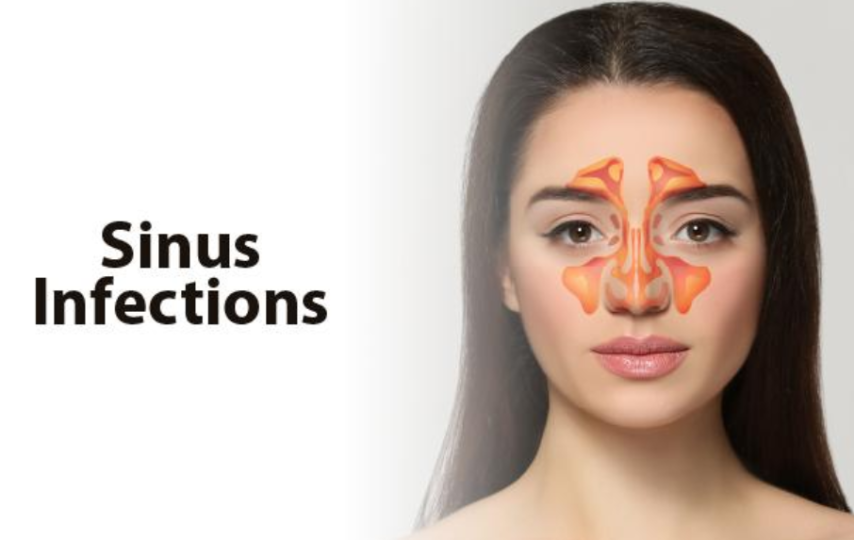
The spaces inside your nose (sinuses) get inflamed and swell up when you have acute sinusitis. Mucus builds up as a result of the obstruction to drainage. It could be challenging to breathe through your nose if you have acute sinusitis. You might feel as though your face and the area surrounding your eyes are enlarged, and you might experience a headache or sharp facial pain.
Colds are the main cause of acute sinusitis. Most instances are over in a week to 10 days, barring the emergence of a bacterial infection. You could only require home remedies to treat acute sinusitis. Chronic sinusitis persists for longer than 12 weeks despite medical treatment.
Signs
Signs of acute sinusitis frequently include:
- Postnasal drainage: the flow of thick, yellow, or greenish mucus from the throat or nose.
- Trouble breathing via your nose due to a congested or blocked nose
- Pain, soreness, swelling, and pressure around your eyes, cheekbones, nose, or forehead that get worse when you lean over.
Other indications and symptoms are:
- Ear discomfort
- Headache
- Your teeth are hurting.
- Alterations to smell
- Cough
- Foul odor
- Fatigue
- Fever.
When to visit a doctor
Most individuals with acute sinusitis don’t require medical attention. Speak with your doctor if you experience any of the following,
- Longer-lasting symptoms (more than a week or so)
- Symptoms that seem to get better but then get worse
- A recurring fever
- A background of persistent or recurrent sinusitis
If you experience any symptoms or signs pointing to a dangerous infection, consult a doctor immediately. You may benefit from an online sinus infection treatment if you experience the following symptoms:
- Eye pain, edema, or redness.
- High fever
- additional vision changes, such as double vision
- Confusion
- A rigid neck.
Risk elements
You may be more susceptible to developing sinusitis if you have:
- Hay fever or another allergic condition affecting your sinuses
- A common cold that causes sinus problems
- An abnormality in the nasal passages, such as nasal polyps, tumors, or a deviated nasal septum
- A sickness like cystic fibrosis or a disease of the immune system like HIV/AIDS
- Exposure to smoke, either directly via smoking or indirectly from secondhand smoke.
Prevention
Follow these recommendations to help lower your risk of developing acute sinusitis:
- Keep upper respiratory illnesses at bay. Try to avoid interacting with those who are contagious or infected with other diseases. Regularly wash your hands with soap and water, especially before eating.
- Take care of your allergies. To keep your symptoms under control, work with your doctor.
- Avoid breathing dirty air or smoking. Your lungs and nasal passages can become irritated and inflamed by tobacco smoke and other contaminants.
- Use a humidifier. Adding moisture to the air in your home may help avoid sinusitis if the air is dry, as it is if you have forced-air heating. Also, ensure thorough, routine cleanings to keep the humidifier clean and mold-free.
THE WRAP-UP
The common cold is the most typical cause of acute sinusitis, a viral infection. Bacterial infection can happen occasionally. You should see a doctor if the infection doesn’t disappear in a week.