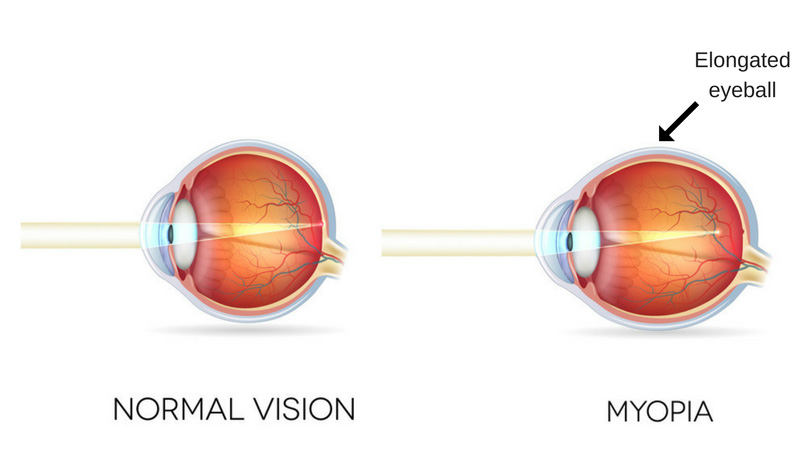
Myopia (nearsightedness) is a popular vision condition whereby you see objects closer to you clearly, but objects that are not near are blurry. This occurs when the shape of the eyes causes light rays to refract incorrectly, focusing on images in front of your retina rather than on your retina. It may develop rapidly or gradually and worsen during childhood and adolescence. Nearsightedness tends to be hereditary.
Causes
The structure of the eye is the main cause. If your cornea, which is the protective layer of the eye, is too curved or your eyeball is too long, the light that gets into the eye will not focus appropriately. Images focus before the light-sensitive parts of the eye (retina) rather than directly on the retina. Check the best eye specialist near me for specialized eye doctors to help with your myopia.
High myopia: this is a severe form of the condition, where you will find the eyeball growing more than it is supposed to and it becomes very long front to back. Other than making it difficult to see objects at a distance, it can also increase your chance of developing other conditions like cataracts, detached retina, and glaucoma.
Degenerative myopia: This is also known as pathological/malignant myopia. This unique type is usually inherited from parents. The eyeballs grow longer and very fast, therefore, causing severe myopia. Usually, it happens in teenage or early adult years. This type of myopia can worsen further into adulthood. Despite making it difficult to see objects at a distance, and according to the Vancouver corrective eye surgery experts it might also increase your chance of developing glaucoma, detached retina, and abnormal blood vessel growth in the eye (choroid neovascularization).
Symptoms
One of the main symptoms is that more distant objects seem to be blurred. One is also likely to experience headaches, eye strain, squinting, and eye fatigue when looking at objects that are more than a foot away. Also, children who suffer from myopia often have difficulty reading the black wall/blackboard at school.
Diagnosis and treatment
An eye examination can show if someone is myopic. Contacts, glasses, and refractive surgery can always correct the problem. When suffering from myopia, your prescription for contact lenses or glasses will be a negative number. If the number is more negative, then the stronger
your lenses. This prescription aids the eye to focus light on the retina, this clears up your vision. Eye surgery may improve your vision so much that you may no longer need to put on contacts or glasses. The most popular surgery for myopia is Photorefractive keratectomy, also known as PRK. It is a type of surgery that a laser is used to sculpt the middle layer of the cornea. It flattens the cornea’s curve and allows light rays to focus on or closer to your retina. Lasik is the other procedure, which is the most common surgery for myopia. Atropine eye drops or special contacts are effective in reducing the progression. In some cases, your eye doctor might suggest clear lens replacement surgery or contacts.
Myopia is a common eye condition that can be confirmed through a simple eye examination. Your eye doctor can easily fix this condition with contact lenses, eyeglasses or refractive surgery to compensate for the blur.